How to Choose HV Connectors and Harnesses for Electric Vehicles

Automotive high-voltage wiring harness (high-voltage cables and high-voltage interfaces) is a key component of the high-voltage electrical system, providing reliable operation and safety of electric vehicles. The main development and design solutions for the whole vehicle high-voltage harness involve cable layout, cable diameter selection, high-voltage connector selection, charging cable and interface types and applications, cable fixing and protection, etc.
The Whole Vehicle Layout of High Voltage Harness
The high voltage connection harnesses between each high voltage component, such as a battery to PDU, motor controller to the motor, AC/DC charging, etc., are reasonably arranged by the layout position of the high voltage components of the electric vehicle.
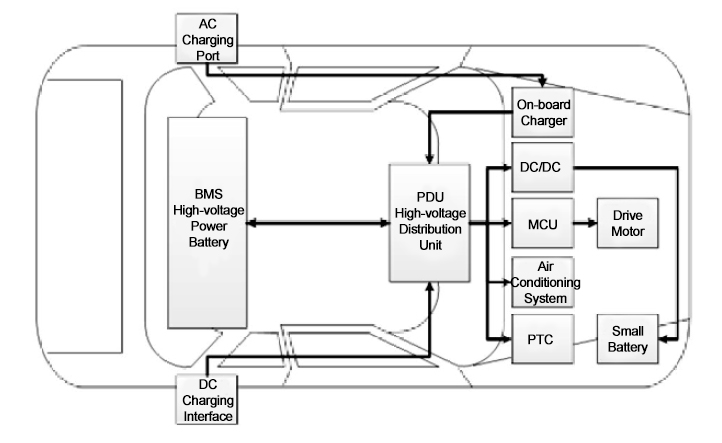

If the high-voltage wire harness needs to pass through the sharp edge of the hole, should design the corresponding protection structure. In the early full vehicle development, harness arrangement must try to avoid the heat source vibration source; otherwise, it should be kept at a sufficient distance. High-voltage wire harnesses have a large outside diameter and weight. To avoid the concentration of stress, the minimum bending radius of the cable is generally greater than the diameter of the wire diameter of 5 times.
To reasonably distribute the load, the need to increase the support of the fixed installation. Wire harness straight line arrangement between fixed points ≤ 300mm; over the bend arrangement, fixed points are fixed at the two endpoints of the arc. Fixed point and connector spacing ≤ 150mm to withstand the weight of the harness and vibration load.
The fixing device must use automotive-grade ties and insulated brackets, etc. The drive motor harness must consider the effects of component movement and vibration. The harness size has to be reasonably designed to meet the stresses distributed in length and avoid harness buildup due to excessive length. For the wire harness movement, increase the rubber ring cushion and guide slot fixed structure to avoid cutting the wire harness and other components, resulting in damage to the wire harness.
The following points should be considered during the wiring harness arrangement
Considering EMC electromagnetic interference factors, shielded high-voltage cables are used to avoid high-frequency noise emission. High and low-voltage cables must be arranged separately to avoid mutual interference caused by cross-overlapping harnesses.
Considering the aesthetics of the harness arrangement, the direction needs to be consistent with the direction of the dependent parts to avoid oblique direction. For the hair cabin wiring harness, as far as possible in the structural parts or components below or inside the alignment, the bottom of the entire vehicle's exposed high-voltage wiring harness uses pipe guards and a shielding plate for shielding protection.
Consider installing and maintaining the same part of the connector to prevent misinsertion by choosing a different specification and positioning method for the connector. The end of the connector needs to leave a certain amount of margin for plugging.
Consider high-voltage safety. This high-voltage electricity has exceeded the human body's safety voltage. The body can not be the same as the low-voltage system of the hitch. It must use a dual-track system.
High Voltage Cable Selection
The cable diameter is according to the layout of each high-voltage electrical component of the vehicle to distinguish the main circuit and branch circuit. And to determine the response characteristics of the high-voltage components connected to the high-voltage wiring harness.

Characteristics include operating voltage, rated power, peak power, rated current, peak current, duration, etc. Operating temperature and ambient temperature also affect the cable diameter. Since high current transmission can lead to high power consumption and related components to increase the temperature rise, thus the high-voltage cable design must withstand higher temperatures. If the cable is arranged in an environment that exceeds the allowable operating temperature of the cable, a cable with a larger cross-sectional area must be selected.
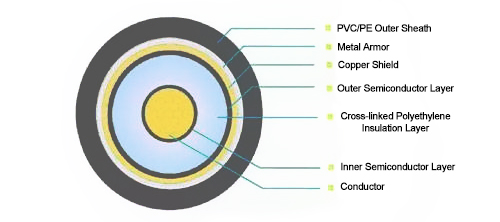
For Tmax up to 180℃, the conductor cross-sectional area will be used in one block. 250℃ Tmax is the conductor cross-sectional area used in two blocks. Cable structure High-voltage cables are divided into single-core cables and multi-core cables. High-voltage cables are round in cross-section and have an orange sheath color. Multi-core cables are made up of multiple single-core wires. Single-core cables must also meet the relevant technical parameters of single-core cables. And if the multi-core cable is used for signal transmission, please use a separate shield to ensure the signal is not lost.
The conductor mainly uses multi-core soft copper-stranded wire to meet the technical requirements of the wire's internal resistance and soft bending degree. The insulation layer must resist high and low temperatures and flame retardant, mostly composite structure. For EMC protection, the high-voltage cable with a shielding layer uses bare copper or copper-plated wire braided on the inner sheath layer with a braiding density of ≥ 90%.
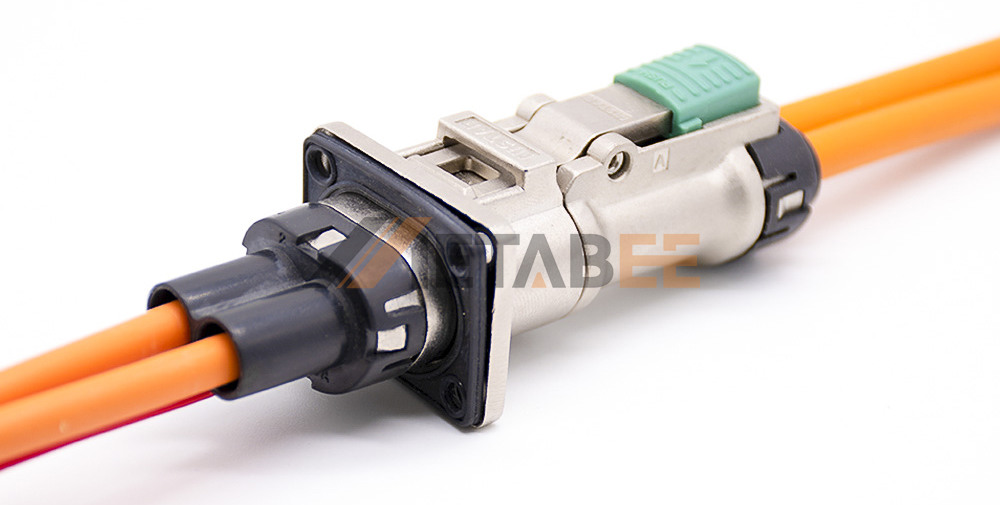
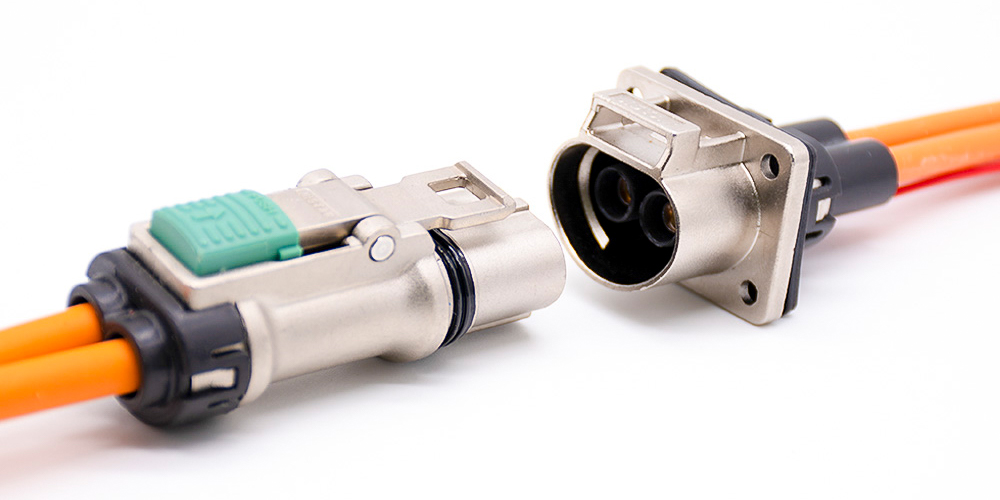
High Voltage Connector Selection
Electrical performance: we need to consider the rated working voltage, rated working current, insulation resistance, voltage withstanding grade, shielding and interlocking, and other related electrical performance parameters.
Environmental performance: we need to consider the requirements of operating temperature, ambient temperature, salt spray level, flame retardant level, and resistance to solution reagents and banned substances.
Mechanical performance: according to different working conditions to test the vibration resistance and the corresponding mechanical life.
Safety performance: high voltage interlock has the built-in type and external type. The built-in type has a compact layout and small size. The built-in type is used on electric vehicles and detects high-voltage interlocks by controllers such as VMS or BMS. To ensure personal safety, the charged part must be reduced to below 60Vd.c and 30Va.c within 1S after separating the high-voltage connector.




Maintenance Switch
The maintenance switch MSD, or manual maintenance switch, is a key component to ensure the high-voltage electrical safety of pure electric vehicles and is an actuating component that can achieve electrical isolation of the high-voltage system at critical moments. It can integrate both the breaking device and the fuse to a high degree. The appropriate fuse is configured internally to protect the circuit from overcurrent and short circuit protection. Proper design and operation of the maintenance switch play a vital role in the electrical safety of electric vehicles.
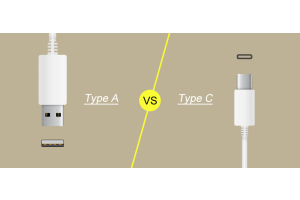
Charging Interface
The charging interface is currently two kinds: AC and DC. The AC interface connects the AC grid power to the vehicle charger through the control and protection device on the cable. The DC interface is a power supply device with a direct control guidance function to the electric vehicle battery.
AC interface rated voltage 250Va.c or 440Va.c, rated current not exceeding 63A. DC interface rated voltage 750Vd.c or 1000Vd.c, rated current not exceeding 250A. The rated voltage and current value of the charging interface are determined according to the requirements of the vehicle layout. Other relevant electrical characteristics and other AC/DC charging interface parameters must meet the requirements of national standards GBT20234.2-2015 and GBT20234.3-2015.
High-voltage Harness Fixing and Protection
High-voltage Wire Harness Fixing
There are various ways to fix the wire harness. According to the arrangement of each high-voltage device of the whole car, reasonably choose how to fix the wire harness or connector. The commonly used tight fixing methods currently include one-piece fixing ties with wedge-shaped fixing heads, ones with cedar-shaped fixing heads, etc., applicable to the round hole way fixing.
One-piece welding stud fixing tie, with welding stud fixing piece isolated double clevis tie, etc., is suitable for welding stud fixing. Fixing ties and clamp-type snap assemblies are suitable for fixing pipes, hoses, wire harnesses, etc.
Plate edge clips are suitable for fixing metal or sheet edges of thickness not exceeding 3mm. Heavy-duty retainers are suitable for wire diameter ≥ 35mm2. Cable conduit supports are suitable for lifting the cable from the frame rail to separate the cable from the protruding body parts to prevent cable wear. Connector snaps are suitable for fixing high-voltage connectors. Bellows snap is suitable for fast-fixing bellows.
High-voltage Wire Harness Protection
Bellows protection: It uses closed-end bellows whose characteristics are wear-resistant, flame retardant, heat-resistant, etc. The temperature resistance of bellows ranges from -40 to 150℃ and can also reach 200℃ for a short time. The common materials on the market are PA (nylon), PE (polyethylene), and PP (polypropylene), respectively. Each has its advantages in terms of flame retardancy, wear resistance, and resistance to bending fatigue. The bellow's color must be orange to distinguish the entire vehicle's low-voltage wiring harness. And use rubber sheath plastic sealing, PVC tape wrapping, and cable fixed seal.
Tube protection: For the wire harnesses arranged in small spaces or special parts, special wire harnesses need to be used to shield and protect. The general pipe guard has stable chemical properties, non-aging, strong corrosion resistance, and other characteristics.
Guard protection: For the high-voltage harnesses arranged in the chassis part (battery total positive and negative) protection method, the design of the guard plate to consider waterproof, anti-sand splash, anti-cuts, and other factors. Most shields use ABS + PC with high impact, high heat resistance, low temperature with high impact strength, and flame resistance.
Sheath protection: parts can be used for easy damage and impact since the rolled sheath. Its characteristics are high-temperature resistance, impact resistance, cut resistance, lightweight and easy installation.
Tape Protection: The tape is used for various applications for wire harnesses. It is often used for protection, bundling, insulation, flame retardant, marking, and other functions. High-voltage wire harnesses are made of flame-retardant PVC tape, which can withstand temperatures up to 80℃.