How Long Can a USB Cable Be?

In today's world, USB has become a widely chosen communication protocol for data transfer between computers and their peripheral devices. Initially, USB was primarily used to connect devices over short distances; however, over time, the use of USB has expanded to encompass long distance applications such as medical imaging, security cameras, and machine vision. For example, when setting up multiple USB security cameras around the house and monitoring them with a single PC, the need for longer USB transmission distances is often beyond the scope of the USB-IF standard.
According to the USB-IF, each USB standard has a clearly defined maximum length, as the signal power decreases as the length of the USB cable increases. Therefore, shorter USB connections are usually more recommended.
USB Standard Length
Different USB versions have different maximum cable length requirements. Both the USB connector type and the length of the USB harness have an impact.
| USB Version | Data Speed | Maximum Permissible Cable Length |
|---|---|---|
| USB 1.0 | 12Mbps | ≤ 3m or 9.8 feet |
| USB 2.0 | 480Mbps | ≤ 5m or 16.4 feet |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1 | 5Gbps | ≤ 3m or 9.8 feet |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2 | 10Gbps | ≤ 3m or 9.8 feet |
| USB 4 | 40Gbps | ≤ 0.8m or 2.6 feet |
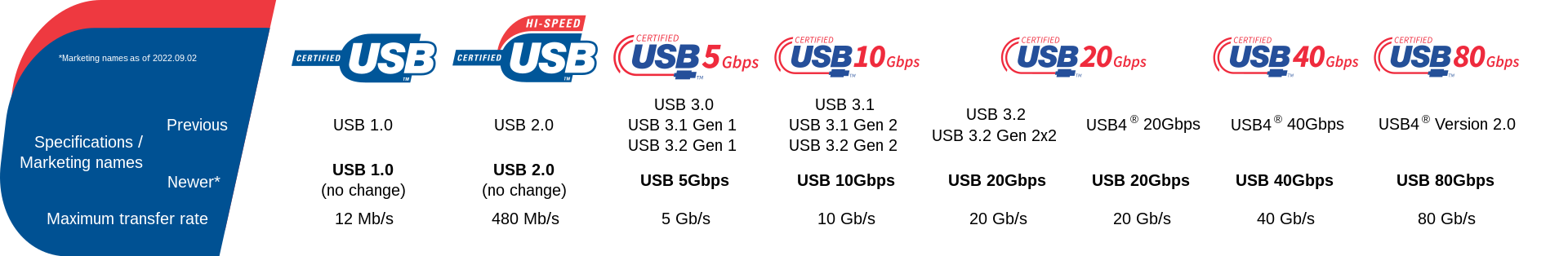

USB 1.0 has negligible speeds and only extends up to 9.8 feet. USB 2.0, on the other hand, has a maximum cable length of 16.4 feet. Also, the successor to USB 3.0 limits the cable length to 9.8 feet. Finally, USB 4 is best suited for very short cable lengths of 2.6 feet. This is probably to avoid signal loss due to long transmission distances.
Disadvantages of Increasing the Length of USB Cables


- Signal Degradation: As the length of the USB cable increases, the electrical signals transmitted over the cable can weaken. This signal degradation may lead to data loss, reduced data transfer speeds, and potential errors in communication.
- Voltage Drop: Longer USB cables can experience a voltage drop, impacting power delivery to connected devices. Insufficient power may result in devices not functioning correctly or charging at a slower rate.
- Data Transmission Errors: Signal attenuation and interference can introduce errors in data transmission. This can manifest things such as corrupt files, intermittent connectivity, or failure to establish a stable connection between devices.
- Limited Power Delivery: USB cables are designed to deliver power to connected devices, but longer cables may struggle to provide sufficient power over extended distances. This limitation can affect the functionality of power-hungry devices.
- Compatibility Issues: Some devices may have stricter requirements for USB cable lengths to ensure optimal performance. Using longer cables beyond the recommended specifications may lead to compatibility issues and hinder the proper functioning of certain devices.
- Interference and Crosstalk: Longer USB cables are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. This can result in a decrease in signal quality and stability, impacting the overall performance of connected devices.
- Non-Compliance with USB Standards: USB standards define maximum cable lengths for different versions (USB 2.0, USB 3.0, etc.). Exceeding these specified lengths may violate USB standards, leading to unpredictable behavior and unreliable connections.
In summary, while it may be tempting to extend USB cable lengths for convenience, it's essential to be aware of the potential disadvantages. Users should consider the specific requirements of their equipment and comply with USB standards.
Reasonable Extension of the Length of the USB Cable
- Use a High Quality USB Cable: Choose a good quality USB cable to ensure the stability of signal transmission. Good quality cables are usually made of better materials and manufacturing process, which helps to reduce signal attenuation and interference in transmission.
- Choose the Right USB Standard: Different USB standards (e.g. USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB-C, etc.) have different maximum cable length requirements. Ensure you that the chosen USB standard is compatible and meets the required length requirements.
- Use an Active USB Extender: Active USB extenders have a built-in signal booster that boosts the signal power before transmission, allowing for longer transmission distances. This is an effective method, especially if more than the standard length is required.


- Consider Using a USB Extension Cable: USB extension cables are an easy solution for connecting directly to a device and providing additional length. Make sure you use a good quality USB extension cable to minimize signal loss.
- Use a USB Hub or USB Splitter: In situations where multiple devices need to be connected, consider using a USB hub or splitter. They can help centralize the management of devices and reduce the length of individual USB cables by connecting them to the computer with shorter USB cables.
- Using Fiber Optic USB Extenders: Fiber Optic USB Extenders utilize fiber optic technology to transmit signals, allowing for longer distances without the effects of electrical signal attenuation. This is an advanced solution for applications that require extremely long transmission distances.
- Use High-Quality Connectors and Adapters: Choose high-quality USB connectors and adapters to ensure a stable and reliable connection. Low quality connectors can lead to signal loss and connection problems.
- Consider Using a USB Ethernet Extender: For connections that require longer distances, consider using a USB Ethernet Extender. They allow USB signals to be transmitted over Ethernet cables for longer distances.
Overall, choosing the appropriate method depends on specific needs and scenarios. Considering the signal quality, device compatibility, and usage scenarios, the most appropriate USB cable length extension solution can be found.