USB-A vs USB-C: What's the Difference?
USB-A, the traditional rectangular connector, is commonly used for older devices, while USB-C offers faster data transfer speeds, reversible plug orientation, and compatibility with newer devices. Other advantages of USB-C include convenience and enhanced transfer speeds.
Consider how much USB ports and connectors enable us to do—it's truly fascinating. First, we can store the contents of thousands of books on a USB flash drive and access them at any time. (Cool, right?) But we also use USB ports to connect a variety of devices, from mobile devices to TVs to computers, making USB one of our most important connectivity standards.
However, USB connectors did not experience a true next-generation evolution for many years, until recently. Now, USB-C has emerged as the successor to the original USB-A connector technology and is set to change everything. What is the story between USB-A and USB-C? Which type of USB hardware is more suitable for your application? Let's start connecting from the basics of these key technologies.

USB type A at a glance
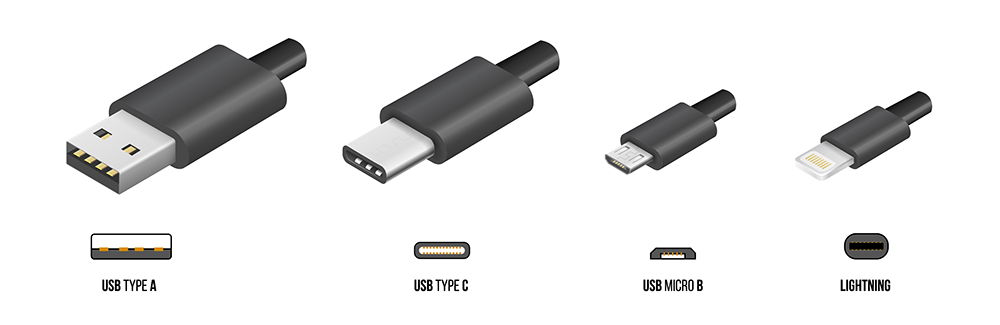
USB-A is the earliest type of USB port, and most people are familiar with it. USB-A ports are common on TVs, computers, and other devices. It's a port on the host device that connects to the recipient device. It can be connected via a USB cable or directly plugged into the recipient device (like a USB flash drive).
USB-A ports have remained popular for so long because they are versatile, reliable, and have been widely deployed on millions of devices worldwide. USB-A technology has been popular for over a decade, with devices like USB flash drives used by almost everyone. The USB 3.0 standard supports USB-A connectors and provides sufficiently fast data transfer speeds to meet most people's needs.
However, USB-A connectors also have some drawbacks. Inserting a USB-A connector can be a bit tricky to align correctly, which can be frustrating. This is because the bottom of the USB-A port has pin connectors that need to be aligned to provide power to the device. Additionally, the data transfer and charging speeds provided by USB-A may not meet the needs of applications that require fast, high-capacity data transfer and/or fast charging.
In conclusion, USB-A is a classic type of USB port with a wide range of applications and compatibility. It is still entirely sufficient for many standard applications. However, for applications that require faster data transfer and charging capabilities, you might need to consider using USB-C or other more advanced USB standards.
USB type C at a glance
It's time to meet USB-C, the next evolution of USB technology (more formally known as USB Type-C). USB-C devices feature a new type of connector that delivers power and data transfer at higher rates. The basic technical standard for USB-C first debuted in 2014, but the technology didn't start to see widespread adoption until the late 2010s.
The first thing you might notice is that the shape of USB-C is quite different from a USB-A port. The USB-C connector is much smaller, more rounded, and symmetrical, meaning it works no matter which way you plug the connector into the port. (A sigh of relief) Despite its different connector shape, USB-C is still backward compatible with USB-A devices with the use of adapters.
However, inside USB-C, it's not just a more convenient port shape, there's more going on. The USB-C standard allows for a series of major improvements over USB-A, including:
- Higher power capacity (known as Power Delivery) for fast charging and powering larger devices.
- The use of alternate modes to be compatible with different connectors (like HDMI ports) when using adapters.
- Faster data transfer capabilities (known as SuperSpeed or SuperSpeed+) through high-speed protocols like USB 3.1 and USB 3.2.
- Support from many large technology manufacturers, including Apple, Samsung, Microsoft, Dell, and more.
One thing you should know about USB-C is that the standard is still evolving. Many different standards have been introduced, such as the USB 3.1 and 3.2 standards we just mentioned. Therefore, when purchasing USB-C devices, it's especially important to check whether they are designed to be compatible with the correct USB standard. Read the USB-C standards to make sure you understand them.
What's happening about USB type B?
From the lack of attention to USB-B, you might think it has disappeared like the iPhone 9. But in fact, USB-B does exist, it's just a more specialized technology that is less commonly used in general commercial and consumer applications. Instead, USB-B is most commonly found in peripheral devices, such as printers and scanners. Therefore, although it's still a relatively common type of connector, most people can go years without having to purchase a USB-B cable.
USB-B connectors have a more trapezoidal shape, completely different from USB-A or USB-C. Devices with USB-B ports are typically connected to USB-A ports via a USB-B to USB-A cable. In addition, there are many other types of USB connectors, such as Micro-USB and Mini-USB, which are specifically used for applications like charging mobile devices. USB-C is designed to replace many smaller connector sizes.


USB-A and USB-C: A Battle of Standards
Now that we have some clear understanding of USB-A and USB-C, it's time to look at a comparison between them. Both of these USB standards have their own advantages, and understanding these will help you make the right choice.
USB-A:
- Broad compatibility: USB-A is currently the most common USB interface, with nearly all computers and devices supporting USB-A.
- Low cost: Due to its widespread use, USB-A devices are typically lower in price.
- Suitable for regular applications: USB-A is sufficient for many everyday home and office applications, especially versions of USB-A like USB 3.0 and higher, which can deliver good performance.
USB-C:
- Reversible plug: The USB-C connector features a symmetrical design that can be inserted in any direction, making it more convenient.
- Enhanced features: USB-C supports higher power transmission and faster data transfer speeds, enabling fast charging and high-speed data transfer.
- Future development: USB-C is the primary connection standard for next-generation technologies, with many new devices adopting USB-C interfaces, it has a better development prospect.
Choosing between USB-A and USB-C depends on your specific needs:
- If you need compatibility with a variety of devices, especially older ones, or are sensitive to cost, USB-A might be a better choice.
- If you need faster charging speeds, higher data transfer speeds, or compatibility with future devices, USB-C might be more suitable for you.
With the stage set for a widespread shift to USB-C in the coming years, more and more businesses are finding that it's worth taking the plunge to benefit from the superior performance specifications of USB-C.
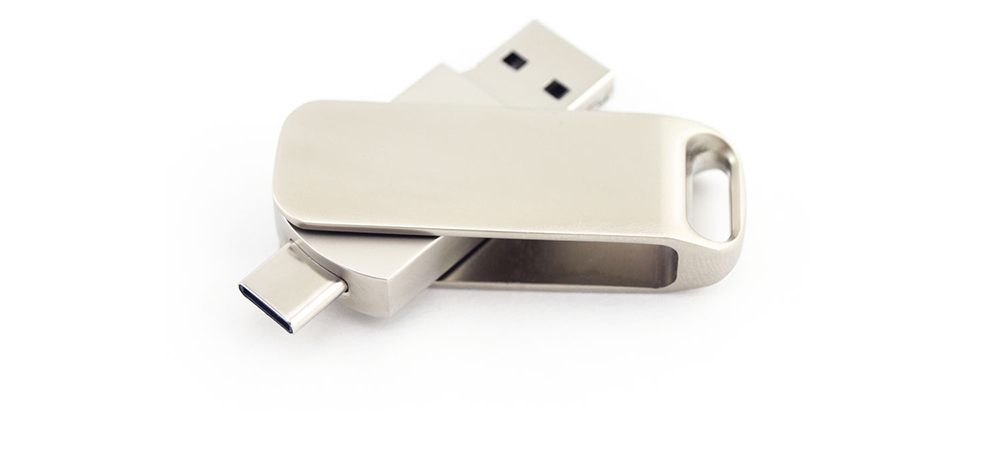
Dual Connector USB Flash Drive
Deciding between USB-C and USB-A can be confusing. While your desktop might only support USB-A, advanced tech companies like Apple have been exclusively supporting USB-C since 2015.
This is where dual-head flash drives shine. They are equipped with a USB-A connector on one side and a USB-C connector on the other. They are particularly useful for promotional events, where flash drives will be distributed to a large and potentially diverse audience, who may use the USB drives across various devices.


What is the present and future of USB type C?
Many technologies are now taking advantage of the enhanced capabilities of USB-C. Some are nearly ubiquitous, while others are still in the early stages.
Currently, USB-C connectors are primarily used as charging ports for mobile devices and laptops. USB-C has an incredible power capacity (up to 240 watts with the latest Power Delivery standard), making it capable of charging anything from smartphones to high-end laptops, which is why you often find USB-C connectors on portable USB power banks.
And what about the new technologies of the upcoming USB standards? USB4 is the latest development in USB-C technology, with great potential for innovation. It is the fastest USB standard so far, with potential data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps. The competing Thunderbolt 3 standard is just as fast. Those seeking the fastest USB performance should keep a close eye on USB4 and Thunderbolt 3, as they are likely to become more widely available soon.