Understanding and Choosing the Right GPS Antenna

A GPS antenna is an antenna that is used to receive signals from the Global Positioning System (GPS). It is usually made of metal materials and has a special design and construction to receive signals from GPS satellites and transmit them to a GPS receiver. a GPS antenna receives signals from multiple satellites and uses the principle of triangulation to calculate the location of the receiver. It is a critical component of the GPS system for positioning, navigation and timing applications.
The GPS satellite signal is divided into L1 and L2 with frequencies of 1575.42MHZ and 1228MHZ respectively, where L1 is an open civilian signal with circular polarization. The signal strength is about 166-DBM, which is a relatively weak signal. These characteristics determine the need to prepare special antennas for the reception of GPS signals. The polarization of the GPS antenna is divided into vertical polarization and circular polarization. With current technology, the effect of vertical polarization is not as good as circular polarization. Therefore, except for special cases the GPS antenna will use circular polarization.
Classification of GPS Antenna
GPS antennas can be classified according to their design and usage.
Built-in antenna: This antenna is usually integrated inside a GPS device, such as a cell phone, car navigation system or handheld GPS device. The built-in antenna is small and lightweight, suitable for portable use, but its reception and directionality may be relatively weak due to the limitations of the device itself.
External antenna: Usually a stand-alone antenna unit that can be connected to a GPS device via a cable. External antennas typically have higher reception and directionality because they can be more flexibly installed in open spaces. External antennas are suitable for applications that require stronger signal reception, such as ships, aircraft or vehicle navigation systems.

Antenna with amplifier: This type of antenna is usually equipped with a low noise amplifier (LNA) to enhance the strength and quality of the received signal. The antenna with an amplifier is suitable for environments with weak signals or high interference, and can provide more reliable signal reception.
Multi-band antenna: This antenna can receive GPS signals from multiple bands at the same time, such as L1, L2, L5, etc. Multi-band antennas can provide more accurate positioning and better interference immunity, and are suitable for high precision positioning applications, such as mapping, military or scientific research.
Dynamic antenna: This antenna has the function of automatic direction adjustment, which can automatically adjust the antenna's direction according to the signal strength and quality to get the best signal reception. Dynamic antennas are suitable for mobile applications, such as vehicle navigation systems or mobile mapping equipment.
Different types of GPS antennas are suitable for different application scenarios and needs. Choosing the right GPS antenna can improve positioning accuracy and signal reliability, thus enhancing the performance of the GPS system.
Construction of GPS Antenna
The construction of a GPS antenna usually includes the following major components:
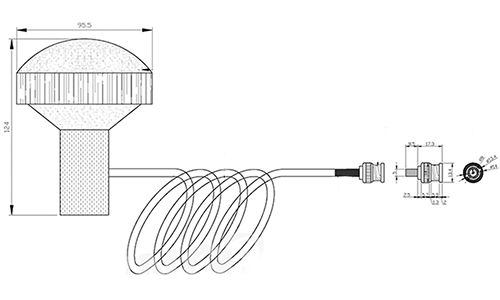

Antenna Components
A key part of receiving and transmitting radio signals. It is usually made of conductive materials, such as metal or conductive coatings. The shape and size of the antenna element affects its frequency response and directionality. Common forms of antenna elements include patch antennas, spiral antennas, pie antennas, etc.
Tuner
Used to match the impedient difference between the antenna element and the receiver to ensure maximum signal transmission efficiency. The tuner usually consists of components such as inductors, capacitors and resistors that can be adjusted according to the frequency requirements of the antenna.
Low Noise Amplifier(LNA)
The LNA is used to amplify the received weak GPS signal to enhance the strength and quality of the signal. The LNA is usually located between the antenna element and the receiver, which can improve the signal sensitivity and anti-interference capability.
Antenna Support Structure
The antenna support structure is used to hold and support antenna elements and other components. It is usually made of plastic, metal or composite materials with sufficient strength and stability to resist the effects of the external environment.
Antenna Connectors
Antenna connectors are used to connect the antenna to the receiver or other devices. Common types of antenna connectors include SMA, BNC, TNC, etc. You can choose the right connector according to the interface requirements of the device.
The above is the general construction of GPS antennas, and different types of GPS antennas may have slight differences. A properly designed and constructed GPS antenna can provide better signal reception capability and performance, thus improving the positioning accuracy and reliability of the GPS system.
Performance of GPS Antenna




The performance of the GPS antenna is critical to the accuracy and reliability of positioning and can be evaluated by these aspects.
Gain: The gain of the GPS antenna determines the sensitivity and range of its received signal. The higher the gain, the stronger the reception capability of the antenna, which can receive weaker GPS signals. Generally speaking, GPS antennas with gain between 2-5 dBi can already meet the needs of most applications.
Directionality: It refers to the ability of GPS antennas to receive signals in different directions. Some GPS antennas have high directivity, which can reduce the influence of multipath effect and interference signals and improve the accuracy of positioning.
Multipath effect suppression: It refers to the reflection and scattering of GPS signals by buildings, terrain and other objects in the process of propagation, which leads to the diversity of signal propagation paths and thus affects the accuracy of positioning. Excellent GPS antenna should have better multipath effect suppression capability, which can reduce the impact of multipath effect on positioning.
Anti-interference ability: GPS signals are easily affected by interference from buildings, trees, electronic devices and so on. Excellent GPS antenna should have good anti-jamming ability, which can reduce the impact of interference on the signal and provide stable positioning performance.
Frequency range: GPS systems usually operate on the L1 band (1575.42 MHz) and L2 band (1227.60 MHz). A good GPS antenna should be able to cover both frequency bands to ensure that the full GPS signal can be received.
Noise factor: Is a measure of the noise performance of the antenna receiving system. The lower the noise factor, the lower the noise of the antenna receiving system, which can provide a higher signal-to-noise ratio and thus improve the accuracy of positioning.
Linearity: Refers to the performance of the antenna under a strong signal environment. Excellent GPS antenna should have good linearity, which can avoid the interference of strong signal on positioning.
Selecting GPS antennas with good performance can improve the accuracy and reliability of positioning. When selecting GPS antennas, key performance indicators such as gain, directionality, multipath effect suppression, anti-interference capability, frequency range, noise factor and linearity need to be considered comprehensively.
Application of GPS Antenna


GPS antennas are widely used in various fields and industries, the following are some common GPS antenna applications.
Vehicle navigation systems: GPS antennas are used in vehicle navigation systems to help locate and navigate vehicles. It can provide accurate location information to help drivers find the best route and destination. GPS antennas can also be integrated with other systems of the vehicle, such as in-car entertainment systems or vehicle tracking systems.
Ship and air navigation systems: GPS antennas play a key role in ship and air navigation systems. They can provide accurate position and heading information to help ships and aircraft navigate and position themselves. In the marine and aviation field, GPS antennas are one of the key navigation devices.
Scientific research and mapping: High precision GPS antennas are used for scientific research and mapping applications. They can provide accurate position and time information for geodesy, crustal movement monitoring, geological exploration, etc. GPS antennas are also widely used in mapping and geographic information systems (GIS).
Military applications: GPS antennas are of great importance in military applications. They can be used for military navigation, target location, UAV control and other tasks. Military GPS antennas usually have higher anti-jamming capability and security requirements.
Personal rositioning and outdoor sports: GPS antennas are also widely used in the field of personal positioning and outdoor sports. For example, GPS watches, GPS running watches, GPS trackers and other devices use GPS antennas to provide accurate location and distance information to help people track, locate and navigate their sports.
GPS antennas play an important role in various applications, helping people to obtain accurate location information and navigation guidance. With the continuous progress of technology, the application areas of GPS antennas will continue to expand and innovate.
Choose the Right GPS Antenna




GPS systems usually operate on the L1 band (1575.42 MHz) and L2 band (1227.60 MHz). Therefore, the GPS antenna selected should be able to cover both frequency bands to ensure that the full GPS signal can be received. The gain of the GPS antenna determines the sensitivity and range of its received signal. Generally speaking, the higher the gain, the stronger the reception capability of the antenna. When choosing a GPS antenna, the required gain range should be determined according to the specific application requirements and environmental conditions.
Size and shape are also an important consideration when choosing a GPS antenna. For applications where space is limited, small size antennas are more appropriate. And for applications that require better directionality and anti-jamming, special shaped antennas, such as antenna arrays, can be selected. In addition, it is also critical to choose GPS antennas with strong anti-jamming capability. Some advanced GPS antennas use special design and filtering techniques that can reduce the impact of interference on the signal.
The installation method also needs to be considered. Some antennas need to be fixed in a specific position or direction, while others can be installed flexibly. It is also important to choose the right antenna for the specific application scenario and installation requirements.