What is the Car OBD Interface

What is OBD
OBD as an acronym, its full name is On Board Diagnostics Chinese meaning: vehicle automatic diagnostic system. This system can monitor the working condition of the engine electronic control system and other functional modules of the vehicle in real time during the operation of the car. If any abnormality is found, it will judge the specific fault according to the specific algorithm. And in the form of diagnostic trouble codes stored in the system memory.
The useful information obtained after the self-diagnosis of the system can provide help for the repair and maintenance of the vehicle. Maintenance personnel can use the car factory special instrument to read the fault code, so that the fault can be quickly located, in order to facilitate the repair of the vehicle and reduce the time of manual diagnosis.
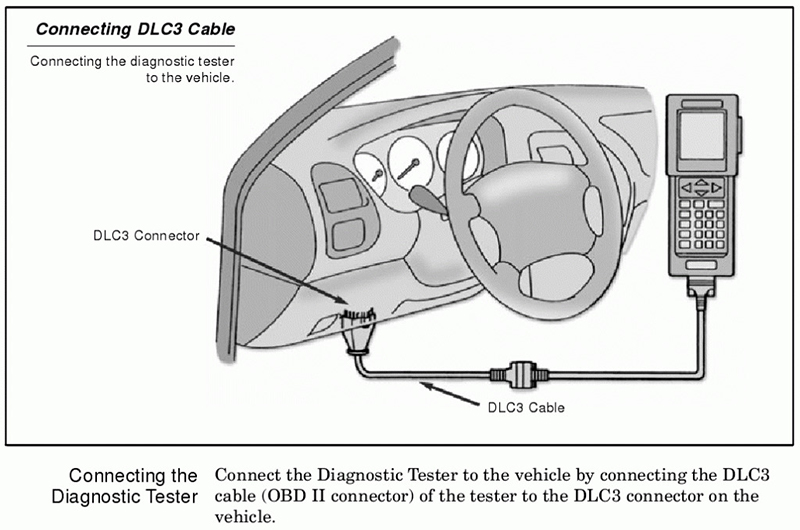

Background to OBD
OBD was created to standardise the diagnosis of emissions and drivability related faults in vehicles. In the United States, since 1996, it has been mandated that new vehicles on the market must have similar diagnostic instruments, trouble codes, and overhaul procedures, and must comply with OBD II procedural requirements.The rollout of OBD II has made automotive troubleshooting simple and uniform, and repairers no longer need to specialise in a particular brand of vehicle's diagnostic system when checking for faults.
The OBD system monitors multiple systems and components on the vehicle, including the engine, catalytic converter, particulate trap, oxygen sensor, emission control system, fuel system, EGR, and more. However, when an abnormality occurs in one of the components, the OBD system will immediately issue an alert. When the vehicle's electronic control system malfunction, the maintenance personnel according to the OBD fault code prompts will be able to quickly determine the nature of the vehicle's fault and fault parts.
OBD-II Interface Package
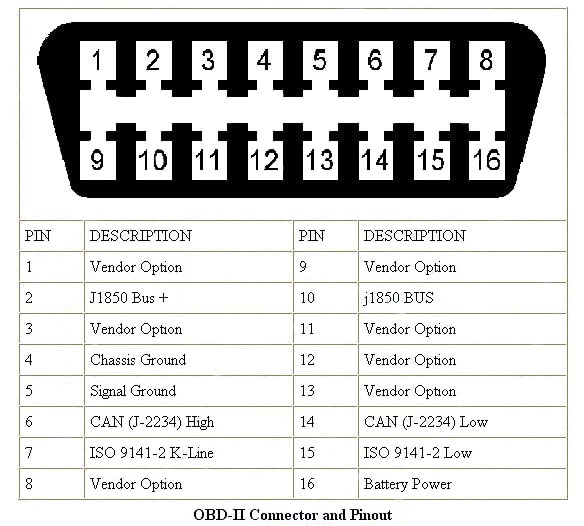
The OBD-Il interface is a T-type interface in a 16-pin package.The pinout of the OBD-II interface is: long side up, short side down, long side 1-8 pins from left to right, short side 9-16 pins from left to right.
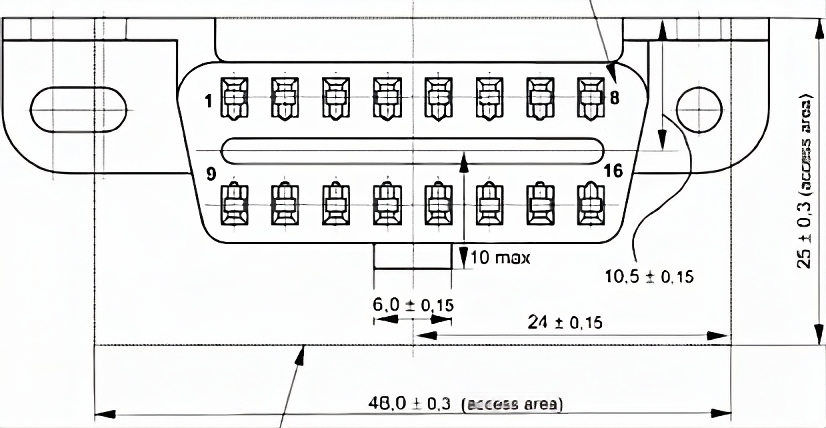

OBD-II Interface Definitions
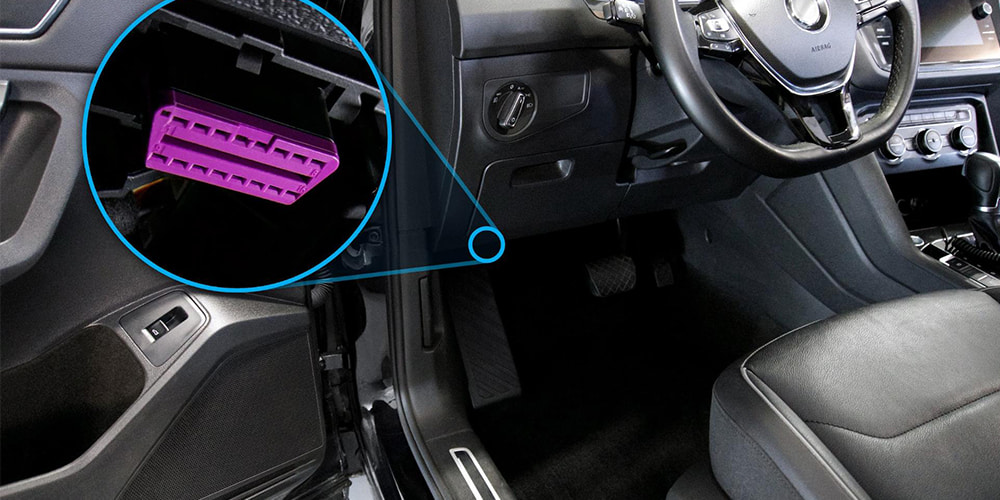
Before we get into the OBD-II interface definitions let's take a look at where the OBD interface is located on most models, and also learn about the main pin definitions of the OBD interface.
In the OBD-II interface, the main pins are 4 pins of Chassis ground: 6 pins of high-speed CAN bus, 7 pins of K communication line, 14 pins of low-speed CAN bus: 16 pins of the power supply positive. In addition to a variety of power and ground and CAN lines outside the interface there are many more, see the following DB-Il interface definition diagram.

Meaning of OBD-Il Error Codes
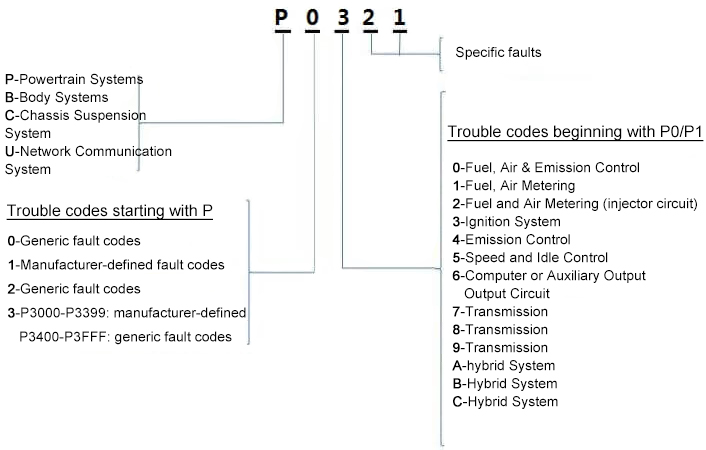

The OBD-II fault code consists of 1 letter plus 4 numbers, the letter represents the system within which the location of the fault is located, e.g. P for Powertrain System, B Body System, C Chassis Suspension System, U Network Communication System, and the letter locates the broader range.
The first number the type of fault code under the specific system, generic fault code or manufacturer customised fault code. The second number represents the specific point of failure, ignition system or transmission and so on. The third and fourth numbers represent the specific type of fault.
OBD-II Applications


The OBD-II communicates with the ECU module via CAN bus, KWP2000 on-board diagnostic protocol, J1850 and IS0 9141 automotive communication protocols. Then OBD-II interface can transmit the information in ECU module to PC or other terminals through USB, RS-232, Bluetooth, WiFi, UART and other technologies to achieve information monitoring or function control of the vehicle.
Such as now on the market in addition to automatic locking, automatic window closing, automatic folding mirrors and other OBD modules, there can be connected to the OBD through a smartphone can not only monitor vehicle information but also has a driving habit monitoring and analysis (such as rapid acceleration, emergency braking and other actions), fault diagnosis, to provide accurate fuel consumption, record the map trajectory, fault rescue, violation of the law query, GPS positioning and other functions of the OBD module.